

Linux volume manager update#
dev/vg001/root: SGI XFS filesystem data (blksz 4096, inosz 256, v2 dirs)įinally, you would update the /etc/fstab so that the logical volumes are mounted at boot. ~]# file /dev/vg001/root -special-files -dereference In Linux, Logical Volume Manager is a device mapper framework that provides logical volume management for the Linux kernel. The file command with the -special-files and -dereference flags can then be used to validate each logical volume has the expected file system type. The mkfs command would then be used to configure each logical volume with a file system type. LV Creation host,time localhost.localdomain, 15:40:12 -0500 LV UUID EuBJ3c-Q8EU0M5ef-Qvip-KeyH-m2Sc-MGelKe
The lvdisplay command can then be used to display each logical volume. Then the lvcreate command is used create logical volumes from available space in the volume group. VG UUID lgHh9m-9iMP-8ltU-2cxz-Y4wL-uwG0-EHiGFr Vertica supports LVM version 2.02.66 or later, and must include device-mapper version 1.02.48 or later. The vgdisplay command can then be used to display the volume group. Linux Volume Manager (LVM) Vertica 12.0.x supports Linux Volume Manager (LVM) on all supported operating systems. Or, if the volume group already exists, the vgextend extend command would be used. In this example, the name of the volume group is "vg001". Next you would use the vgcreate command to add the physical volumes to a volume group.

PV UUID bW0moV-MWxi-4PvP-RWXR-NUFe-GfJD-2fe83A PV UUID qIJr3I-uokW-qIRJ-Mi9a-SmIp-2DYN-XwxUDf Or, the pvcreate command can be used to create the physical volumes. The pvdisplay command should now show both physical volumes.
Linux volume manager how to#
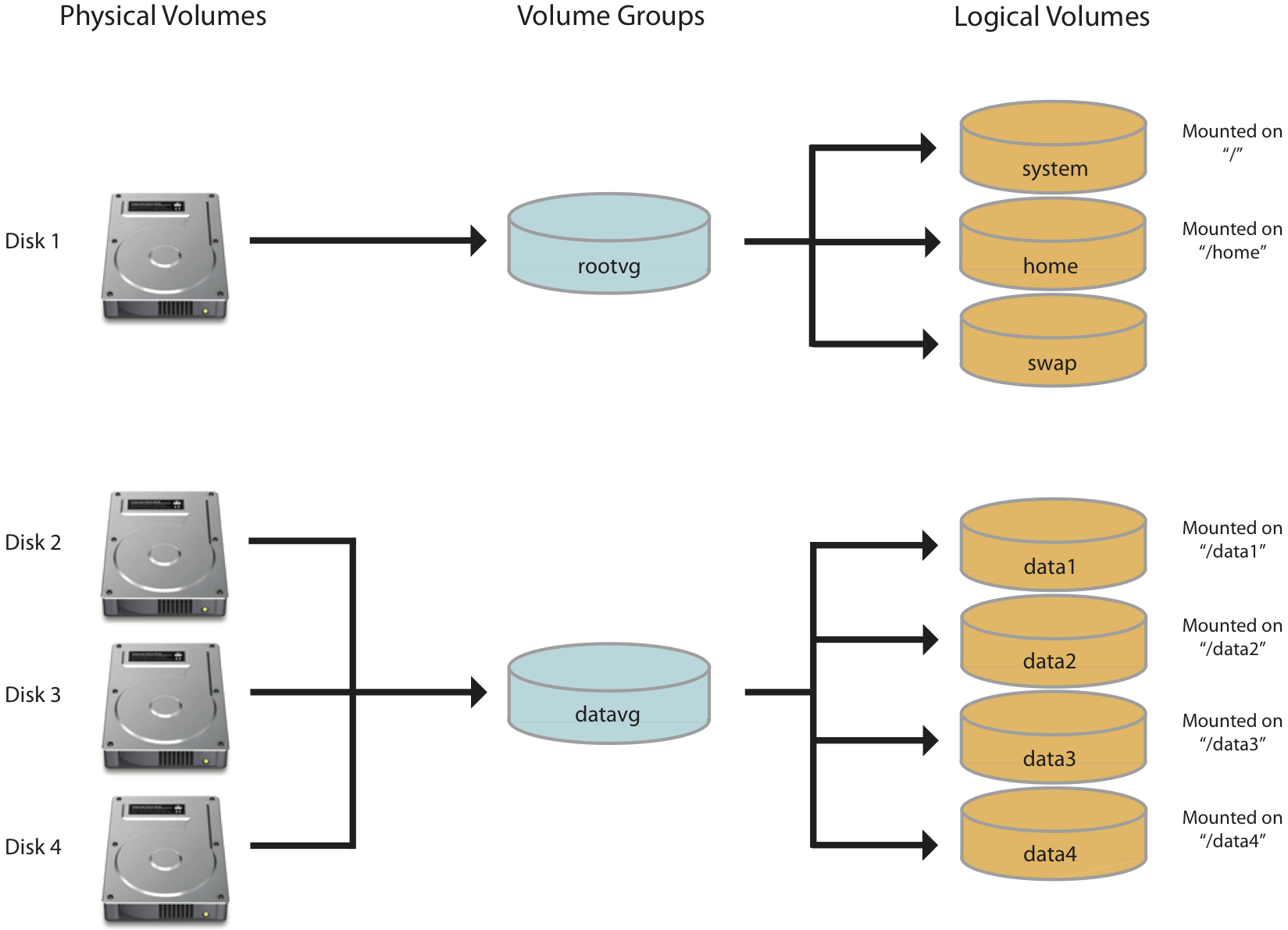
Here are the steps on how to set /dev/sda3 to type Linux LVM using parted. The first step in setting up an LVM system is to create a partition on each physical storage device to use the Linux LVM system. This can be accomplished with fdisk, gdisk, or parted. For example, in this illustration, using 2 physical storage devices, 3 logical volumes are created: The logical volume manager introduces extra layers of abstraction between the disks or storage devices presented to a. LVM (Logical Volume Manager) is a system that lets you create logical volumes from physical storage devices.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
